Psoriasis: Causes, Treatment Methods And Risk Factors
Psoriasis, which is classified as an autoimmune (affecting the immune system) disease, is defined as a condition in which skin cells in the body multiply 2-3 times faster than normal.
The life cycle of skin cells is around 30 days in people who do not have any disease.
However, in people suffering from psoriasis, the time for cells to die and reappear may be reduced to a few days.
T lymphocyte cells in the immune system of people with psoriasis accumulate on the skin.
And as a result of this situation, the time of death and regeneration of skin cells accelerates.
Since the life cycle of skin cells is accelerated, the appearance of the skin begins to differentiate and red spots with a bumpy structure begin to appear on the patient’s skin.
The reason for this is that there is not enough time to remove cells that have completed their lifespan much faster than normal from the body.
Thus, hard plaques form on the skin. In addition to redness of the skin, people with psoriasis also experience the condition of covering the skin with white scales.
Said spots and white scales can appear all over the body.
The most common places where spots are seen are areas of the body such as knees, back, hands, feet, neck, facial skin, scalp and elbows.
What Will We Learn?
What Are The Causes Of Psoriasis?
Today, the factors that cause the emergence of psoriasis have not yet been clarified.
Experts working on the disease stated that psoriasis occurs with the combination of many different factors.
In addition, it is widely believed that various genetic disorders and problems related to the immune system trigger the disease.
While psoriasis can sometimes be seen in people in the same family, it can sometimes occur without any genetic link.
While a mother and her child may be affected by psoriasis, the child’s grandparents may not have psoriasis. As it can be understood from here, it would not be correct to base the origins of the disease entirely on genetic factors.
We can list the factors that can cause psoriasis as follows:
- Genetic factors. In various cases, it has been observed that psoriasis occurs in people who are of the same lineage and close relatives. There is no clear data showing how much the disease is transmitted to other generations. However, it is known that genetic factors constitute a basis for the formation of psoriasis.
- Excessive alcohol consumption and regular use of tobacco products (including passive or active smoking).
- In addition to its psychological effects, psychological problems such as stress, depression and anxiety, which have physical effects and negatively affect the immune system, can also trigger psoriasis.
- Experiencing various traumas on the skin, cuts and abrasions on the skin.
- Surgical interventions on the skin.
- The use of blood pressure medications that fall under the category of beta-blockers, various types of drugs used in the treatment of the bipolar disorder, hydroxychloroquine, and various drugs that fall into the category of “malaria drugs” in general.
- Throat infection, pharyngitis, or various infections that may occur on the skin can also trigger psoriasis.
- Living in a place with a cold or dry climate. As it is known, psoriasis occurs more frequently in the winter when the weather is cold. Extremely hot weather can also trigger the symptoms of psoriasis. If the skin comes into direct contact with extremely hot air, a person may get sunburned, and this is one of the causes of psoriasis.
- Having diseases that adversely affect the immune system of the person. In addition to these diseases, abnormal activity of white blood cells, which are the building blocks of the immune system, can also cause psoriasis.
What Are The Symptoms Of Psoriasis?
The most commonly known symptoms of this disease are reddening and scaling of the skin.
However, this skin disease has multiple different types.
Symptoms of the disease also vary depending on which type of psoriasis the person has.
Listed below are the most common symptoms of this skin disease condition:
- Psoriasis rheumatism (psoriatic arthritis), that is, swelling and pain in the joints can be seen. This condition causes chronic pain in the joints and needs to be treated.
- An image that appears in many parts of the body (knees, elbows, scalp, scalp, genitals, neck, etc.) and whose borders are clearly defined by the formation of redness is dominant. At the same time, psoriasis-colored crusts form in these areas with unusual redness.
- People who have spread the disease on the hair and scalp may experience severe hair loss.
- Tiny pits appear on the nail that can be seen with the naked eye. The nail may thicken and turn yellow.
- Obesity, diabetes and cardiovascular diseases may occur in people with this skin problem.
- There is a severe itching sensation in the skin.
- Various wounds and cracks occur on the skin. The skin is prone to bleeding at the slightest blow.
What Are The Types Of Psoriasis?
This skin disease occurs in five different forms: plaque psoriasis, guttate psoriasis, pustular psoriasis, nail psoriasis, erythrodermic psoriasis and protiatic arthritis.
The symptoms of the disease in the person differ according to the type of the disease.
Plaque Type Psoriasis
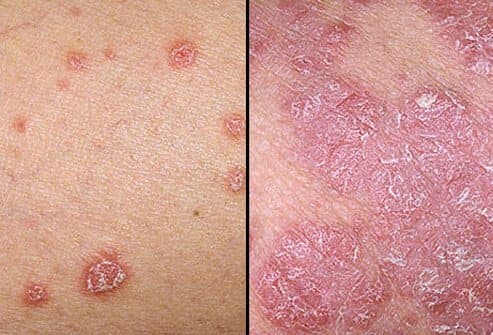
Plaque psoriasis, also known as psoriasis Vulgaris, is the most common psoriasis subtype.
In this subtype seen in 8 out of 10 patients, the skin surface was covered with silvery scales. In addition, red-colored plaques with a dry and thick structure are seen in the same area.
Conditions such as itching, pain, cracking and bleeding are frequently seen in the area of plaque formation.
These plaques can occur in separate areas of the skin and can sometimes grow and merge if they progress untreated.
This type of psoriasis usually occurs on the knees, elbows, scalp and lower back.
Guttate Psoriasis
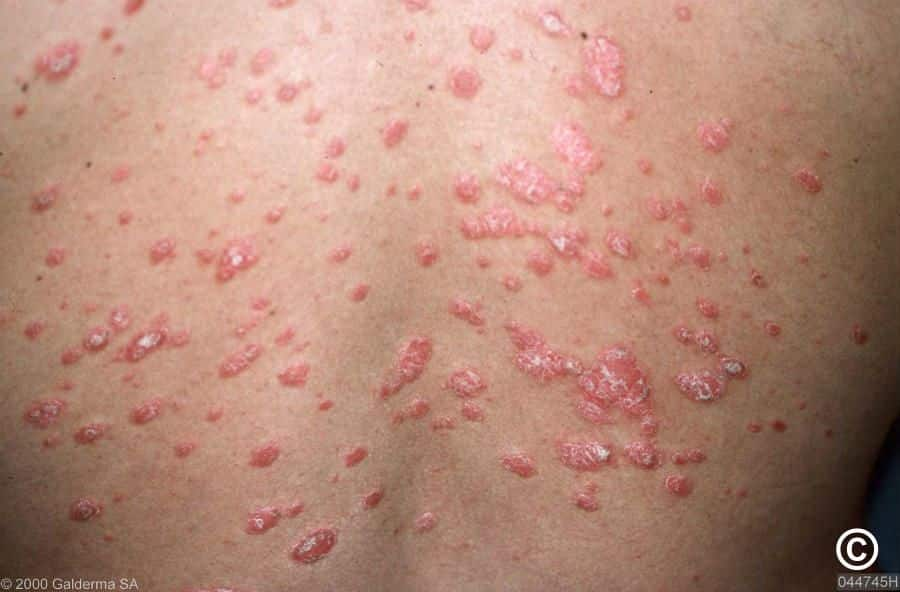
This type of psoriasis usually affects children and young people. It occurs in approximately 1 in 10 patients.
In the type of guttate psoriasis, the rash that occurs on the skin is thinner compared to plaque psoriasis.
Its main distinguishing feature is the formation of drop-shaped lesions on the skin.
Guttate psoriasis usually occurs as a result of bacterial respiratory tract infections, tonsillitis and use of beta-blocker type drugs.
Pustular Psoriasis
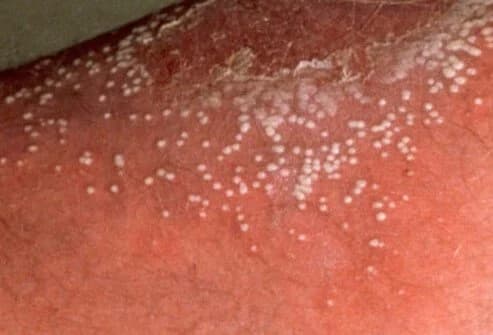
In this type of disease, lesions can occur in any part of the body, especially in smaller areas such as the palms and soles.
Lesions covering a small area at first may enlarge over time, and dandruff may occur on the skin. The distinguishing feature is that the lesions are filled with pus.
At the same time, in the period when the disease is active and pustule-like structures are formed, the person may have a fever, chills, and severe weakness.
Erythrodermic Psoriasis
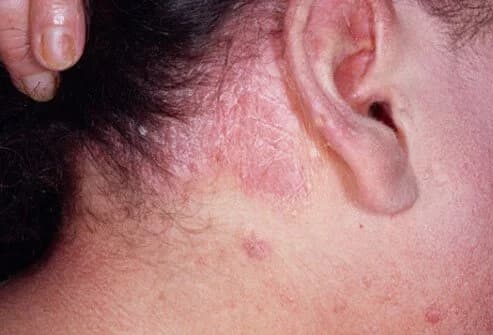
Erythrodermic psoriasis is not a very common subtype. In this subtype, lesions resembling sunburn occur in the person, and these lesions can cover a very large part of the body when active. In this case, the disease can be quite severe and the person may need urgent intervention.
Nail Psoriasis
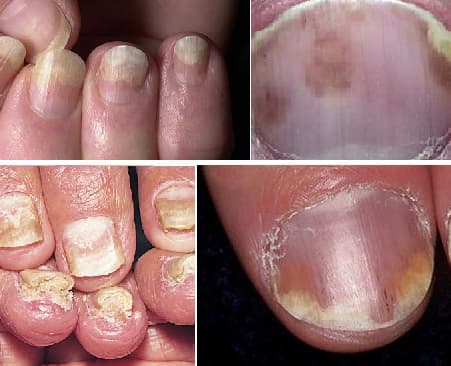
In this type, conditions such as pitting, discoloration, thickening and nail growth can be seen in the finger or toenails of the patient. In cases where treatment is delayed, the nails may crumble or become dislodged.
Psoriatic Arthritis
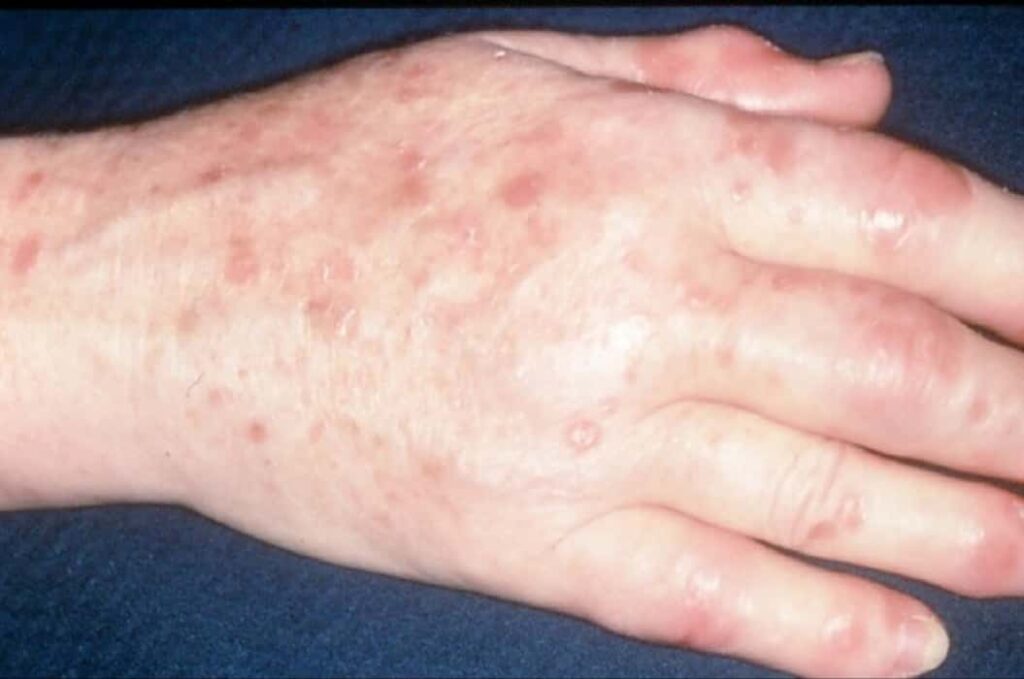
In this subtype, which affects approximately 30% of psoriasis patients, the joint areas of the body are mainly damaged.
There is severe pain in the joints and the joints may begin to swell.
Depending on the severity of the disease and whether treatment is done, even permanent joint damage can be seen in the person.
Joint pain is usually seen in the hands or feet.
However, other large joints are also at risk of being affected.
What Are The Diagnostic Methods?
A lot of tests are not required for the diagnosis of psoriasis. Physical examination is usually sufficient to detect the disease. However, in some cases, biopsy can be applied to distinguish it from other skin diseases that are similar to psoriasis.
How Does Psoriasis Progress?
Psoriasis is a disease that flares up for a while and then gets better. The patient, who has severe symptoms for a few months, may enter a recovery period for several months or several years after this period. However, the duration of the recovery and exacerbation periods varies from person to person and according to the type of disease.
How Is Psoriasis Treated?
Today, psoriasis is unfortunately not a disease that can be completely treated and eliminated.
However, thanks to the treatment methods applied, the symptoms of the disease in the person’s body can be reduced to a great extent.
There are many different treatment methods available for the treatment of the disease. Which method to use depends on the preference of the patient, the severity and type of the disease.
Since psoriasis is not a completely curable disease, the treatment to be applied will also be a long-term treatment.
The products listed below are used in the treatment of the disease:
- Medicines containing cortisone
- Vitamin D
- Shampoos and moisturizers produced with disease-specific ingredients
- Skin creams
- Needles made at regular intervals
- Various drugs and light therapy (phototherapy)
Thanks to these treatment methods, the activities of the cells that cause the disease are reduced and the symptoms are relieved.
In addition to the medical treatment methods mentioned, one should keep morale and motivation as high as possible and try to live a stress-free life.
Therefore, it will be extremely beneficial for the patient to consult a psychiatrist in addition to the treatments to be applied by the dermatologist.
The patient can do various activities such as various breathing exercises, yoga, listening to music and meditation to relax himself at home.
You can also read our informative article on arthritis.
